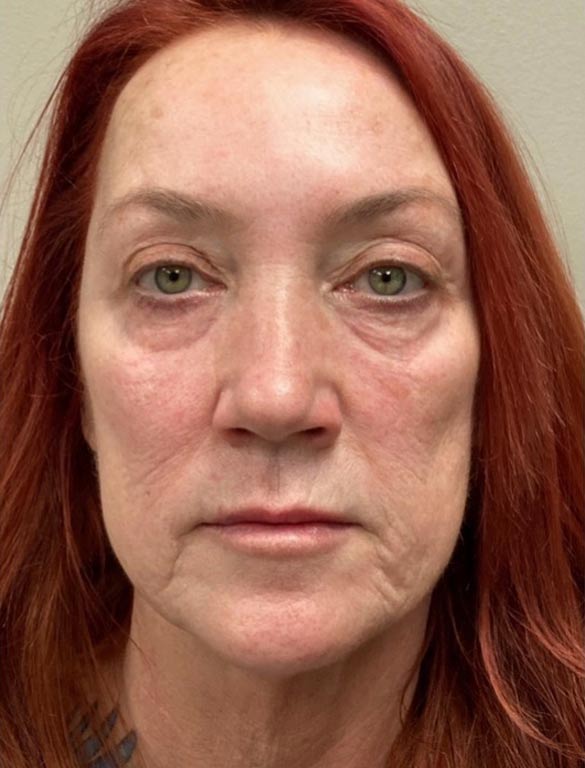
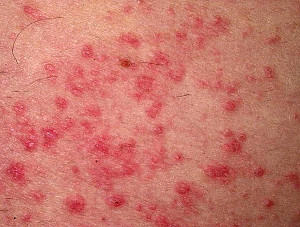
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that usually affects the scalp. It can cause red skin, stubborn dandruff and scaly patches. It is also a condition that can affect oily areas of the body, such as the face, back, and upper chest. It can also cause a condition known as “cradle cap” in infants. It is also called seborrheic psoriasis, seborrheic eczema, and dandruff.
There are a number of factors that increase your risk of developing seborrheic dermatitis including:
- ~A weakened immune system
- ~Congestive heart failure
- ~Neurological and psychiatric conditions
- ~Endocrine disease
- ~Certain medications
Symptoms of Seborrheic Dermatitis and Treatment
- ~Skin flakes on your scalp, hair, eyebrows, beard or mustache
- ~Patches of greasy skin covered with flaky yellow or white scales. Crust on the scalp, ears, face, chest, armpits, scrotum or other parts of the body
- ~Red skin
- Redness or crusting of the eyelids with possible itching or stinging
While seborrheic dermatitis will not affect your overall health, it can be uncomfortable and embarrassing. You should understand that it is not a sign of poor personal hygiene nor is it contagious.
Seborrheic dermatitis is also a long-term condition, requiring repeated treatments. Additionally, the symptoms may return later.
You can manage flare ups by recognizing the symptoms and using a combination of medications and self-care.
There are several home remedies that may help you control this condition including:
- ~Washing your hair with medicated anti-dandruff shampoo
- ~Applying mineral or olive oil to your scalp to soften and remove scales
- ~Applying a mild corticosteroid cream
- ~Avoiding products containing alcohol as these can cause flare ups
- ~Consider shaving off a beard or mustache
You should consult with a doctor if any of the symptoms cause:
- ~Sleep loss or being distracted from daily routines due to uncomfortable symptoms
- ~Embarrassment or anxiety
- ~Skin infection
- ~Unsuccessful self-care treatments
During your exam, your physician may scrape off skin cells for examination to rule out conditions that have similar symptoms. These conditions can include psoriasis, eczema and rosacea.
Medical treatments for seborrheic dermatitis can include:
- ~Prescription-strength shampoos, ointments or creams that control inflammation
- ~Antifungal shampoo that is alternated with stronger medication
- ~Antifungal medications taken orally
- ~Medications that affect your immune system
- ~Creams and gels that fight bacteria
- ~Light therapy in addition to medication